Stories

- Article
Why gene editing can never eliminate disability
In a world where DNA testing and gene editing offer ways to eliminate certain disabilities, Jaipreet Virdi explores a more accepting and inclusive approach.

- Article
Mistakes and perfect medicine
This week our anonymous GP reflects on how a mistake made in a busy, stressful environment could have had serious consequences.

- Article
Why even plastic surgery can’t hide you from facial recognition
Once upon a time, plastic surgery allowed a few notorious criminals to evade the law. But today, sophisticated facial-recognition technology has turned dreams of anonymity to dust.

- Article
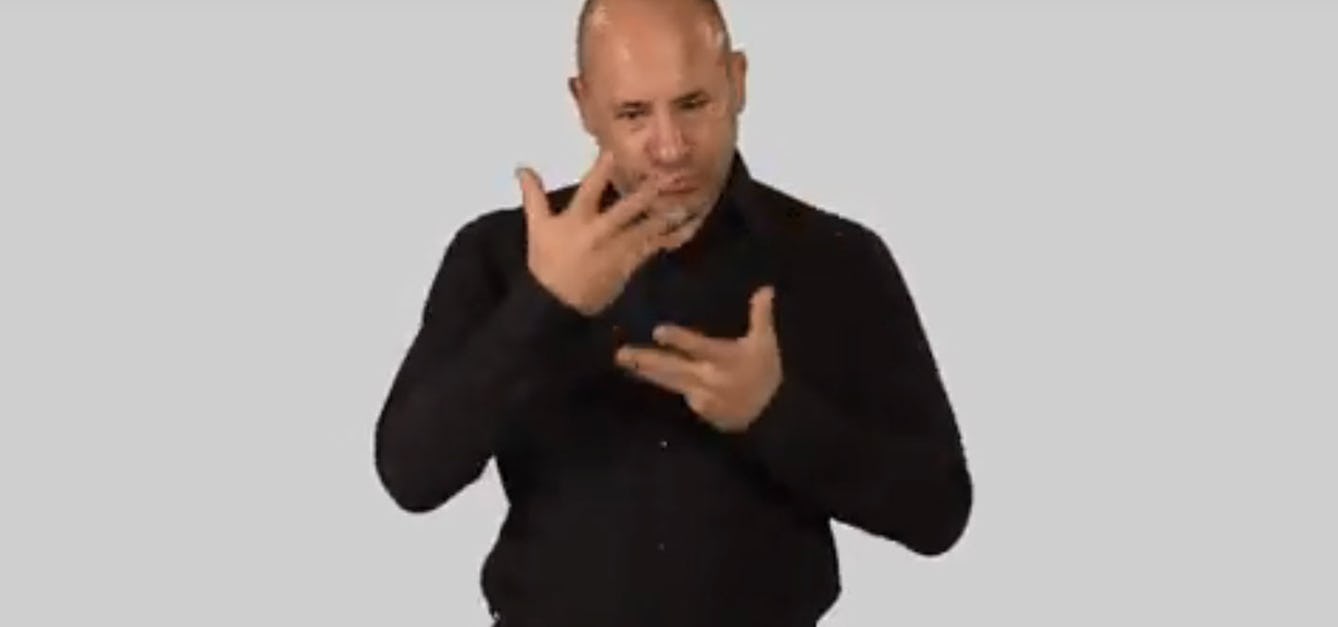
Interpreting the Ayurvedic Man
A British Sign Language video is the latest interpretation of an unique 18th-century Nepali painting about Ayurvedic medicine.
Catalogue
- Books
Medical errors and medical narcissism / John Banja.
Banja, John D.Date: 2004- Archives and manuscripts
- Online
Notes on Errors
Date: 1955Reference: PP/CRI/B/3/3Part of: Francis Crick (1916-2004): archives
- Books
- Online
Medical errors : fallacies connected with the application of the inductive method of reasoning to the science of medicine / by A.W. Barclay.
Barclay, A. W. (Andrew Whyte), 1817-1884.Date: 1864- Archives and manuscripts
James Bower Harrison Popular Medical Errors, addenda
Harrison, James Bower, FRCS (d. 1890)Date: c. 1852-1881Reference: MS.8482
- Archives and manuscripts
- Online
Graph referenced as "Errors"
Davies, Howard G.Date: April 1953Reference: KDBP/1/1/0948Part of: King's College London Department of Biophysics