Stories

- Article
Illness and the influence of the stars
Could alien germs from space have caused major pandemics across the world? Taras Young investigates the ideas of a few unconventional scientists who believe this to be the case.

- Article
The tale of the toxic kidneys
In 1954 a serendipitous coming together of skills and circumstances allowed the first successful organ transplant to take place. Read how Richard Herrick’s life was prolonged by his identical twin’s generosity.
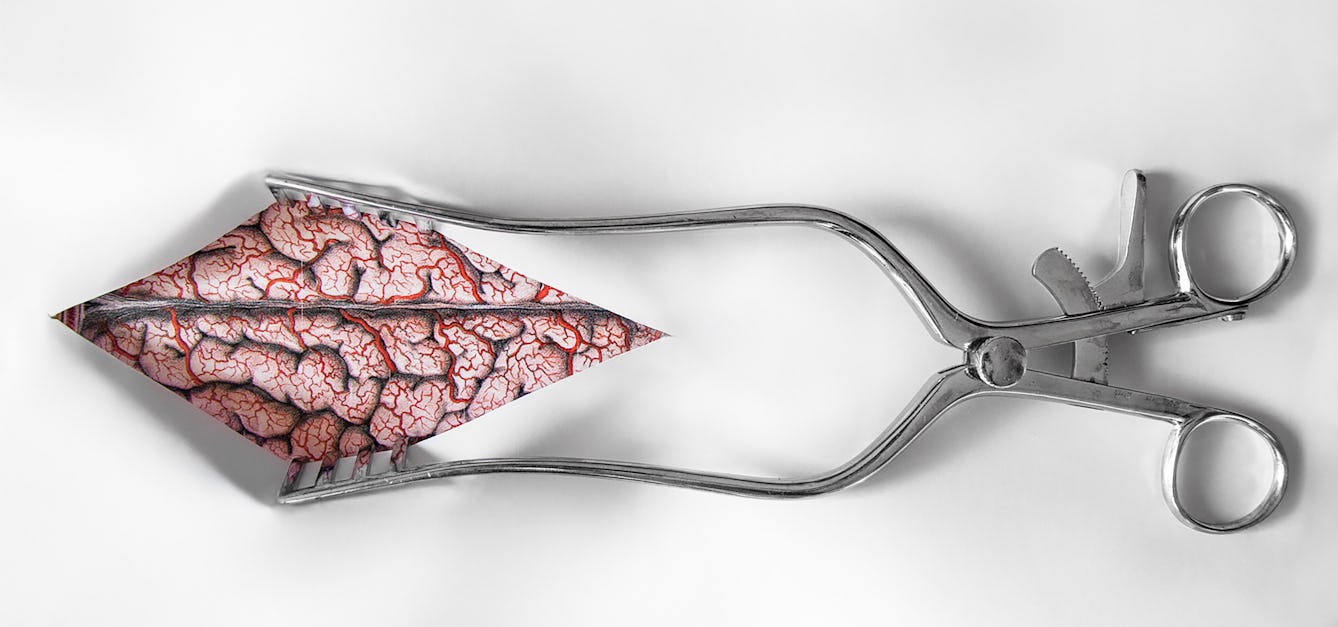
- Article
The mystery of the malignant brain
In 1884 a neurologist successfully used a patient’s symptoms, plus a new kind of map, to locate a brain tumour. Discover how his best-laid plans for treatment worked out.

- Long read
The ambivalence of air
Daisy Lafarge investigates the effects of air quality and pressure on body and mind, exploring air as cure, but one with contradictions.
Catalogue

- Books
- Online
A clinical report of the Royal Dispensary for Diseases of the Ear : with remarks on the objects and utility of the institution / by John Harrison Curtis.
Curtis, John Harrison, 1778-approximately 1860.Date: 1827
- Books
- Online
A clinical report of the Royal Dispensary for Diseases of the Ear : with remarks on the objects and utility of the institution / by John Harrison Curtis.
Curtis, John Harrison, 1778-approximately 1860.Date: 1830
- Books
- Online
A clinical report of the Royal Dispensary for Diseases of the Ear : with remarks on the objects and utility of the institution / by John Harrison Curtis.
Curtis, John Harrison, 1778-approximately 1860.Date: 1827
- Books
- Online
Eighteenth report of St Mark's Ophthalmic Hospital and Dispensary for Diseases of the Eye and Ear, Lincoln-place, 1863-'64.
St Mark's Ophthalmic Hospital (Dublin, Ireland)Date: 1864
- Books
- Online
Eighth report of St Mark's Ophthalmic Hospital and Dispensary for Diseases of the Eye and Ear, Lincoln-place, 1853-'54.
St Mark's Ophthalmic Hospital (Dublin, Ireland)Date: 1854






![Pulsatilla vulgaris Mill. Ranunculaceae Distribution: Europe. Lindley (1838) and Woodville (1790) knew this as Anemone pulsatilla, the common name being Pasque (Easter) Flower. At the end of the 18th century it was recommended for blindness, cataracts, syphilis, strokes and much more, treatments which, as was clear to physicians at the time, were valueless. Gerard (1633) writes: ‘They serve only for the adorning of gardens and garlands, being floures of great beauty’. It is in the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae, all members of which are poisonous. It was recommended, by mouth, for ‘obstinate case of taenia’ (tapeworms). One hopes it was more toxic to the worm than the patient. Flowers with a central disc and radiating florets were regarded as being good for eye complaints under the Doctrine of Signatures. Porta (1588) writes (translated): ‘Argemone [Papaver argemone], and anemone, have flowers of this shape, from this they cure ulcers and cloudiness of the cornea’. There were occupational diseases even before there were words like pneumoconiosis, and Lindley writes that ‘the powder of the root causes itching of the eyes, colic and vomiting, if in pulverising it the operator do not avoid the fine dust which is driven up.’ Photographed in the Medicinal Garden of the Royal College of Physicians, London.](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/B0009141/full/282%2C/0/default.jpg)
![Pulsatilla vulgaris Mill. Ranunculaceae. Pasque flower. Distribution: Europe. Lindley (1838) and Woodville (1790) knew this as Anemone pulsatilla, the common name being Pasque (Easter) Flower. At the end of the 18th century it was recommended for blindness, cataracts, syphilis, strokes and much more, treatments which, as was clear to physicians at the time, were valueless. Gerard (1633) writes: ‘They serve only for the adorning of gardens and garlands, being floures of great beauty’. It is in the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae, all members of which are poisonous. It was recommended, by mouth, for ‘obstinate case of taenia’ (tapeworms). One hopes it was more toxic to the worm than the patient. Flowers with a central disc and radiating florets were regarded as being good for eye complaints under the Doctrine of Signatures. Porta (1588) writes (translated): ‘Argemone [Papaver argemone], and anemone, have flowers of this shape, from this they cure ulcers and cloudiness of the cornea’. There were occupational diseases even before there were words like pneumoconiosis, and Lindley writes that ‘the powder of the root causes itching of the eyes, colic and vomiting, if in pulverising it the operator do not avoid the fine dust which is driven up.’ Photographed in the Medicinal Garden of the Royal College of Physicians, London.](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/B0009140/full/600%2C/0/default.jpg)
![Pulsatilla vulgaris Mill. Ranunculaceae Pasque flower. Distribution: Europe. Lindley (1838) and Woodville (1790) knew this as Anemone pulsatilla, the common name being Pasque (Easter) Flower. At the end of the 18th century it was recommended for blindness, cataracts, syphilis, strokes and much more, treatments which, as was clear to physicians at the time, were valueless. Gerard (1633) writes: ‘They serve only for the adorning of gardens and garlands, being floures of great beauty’. It is in the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae, all members of which are poisonous. It was recommended, by mouth, for ‘obstinate case of taenia’ (tapeworms). One hopes it was more toxic to the worm than the patient. Flowers with a central disc and radiating florets were regarded as being good for eye complaints under the Doctrine of Signatures. Porta (1588) writes (translated): ‘Argemone [Papaver argemone], and anemone, have flowers of this shape, from this they cure ulcers and cloudiness of the cornea’. There were occupational diseases even before there were words like pneumoconiosis, and Lindley writes that ‘the powder of the root causes itching of the eyes, colic and vomiting, if in pulverising it the operator do not avoid the fine dust which is driven up.’ Photographed in the Medicinal Garden of the Royal College of Physicians, London.](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/B0009139/full/282%2C/0/default.jpg)