Stories

- Article
Yoga gets physical
Modern yoga owes a debt to the physical culture movement that created a world obsessed with health and fitness.

- Article
Guide dogs or good dogs from the Middle Ages
Medieval illustrations often show blind people, sometimes with dogs. But working out whether these were actually guide dogs involves a mix of detailed detective work and expert speculation.

- Article
How architecture builds a profession of stress
Architects might produce buildings that enhance our health, but at what cost? Kristin Hohenadel explores architecture’s pressurised and stressful culture.

- In pictures
In pursuit of purity
Many cultures associate physical cleanliness with spiritual purity, while disease and dirt are signs of moral pollution.
Catalogue

- Ephemera
- Online
Quality control : Turpin aim to maintain the highest standards in order fulfilment and despatch... / Turpin Distribution Services Limited.
Turpin Distribution Services.Date: [1993?]- Books
- Online
An account of the land-carriage fish-undertaking, continued by Grant and Company
Grant and Company (London, England)Date: 1768]- Ephemera
Your eyesight isn't too good, but there's nothing wrong with your reflexes! / Bamforth & Co., Ltd.
Date: [between 1970 and 1979?]- Books
Poverty, food security and sustainability : public distribution system in Inda / Bhaskar Majumder.
Majumder, BhaskarDate: [2004]- Film
One of them is Brett.
Date: 1965
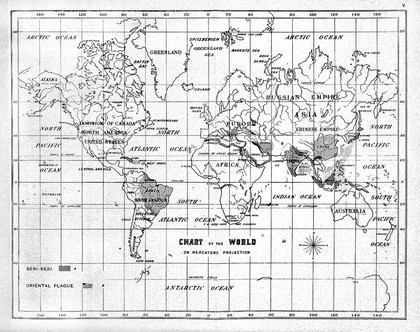
![The physical atlas; a series of maps illustrating the geographical distribution of natural phenomena / [Heinrich Karl Wilhelm Berghaus].](https://iiif.wellcomecollection.org/image/L0077829/full/420%2C/0/default.jpg)