Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
You can use this work for any purpose, as long as it is not primarily intended for or directed to commercial advantage or monetary compensation. You should also provide attribution to the original work, source and licence. Read more about this licence.
Credit
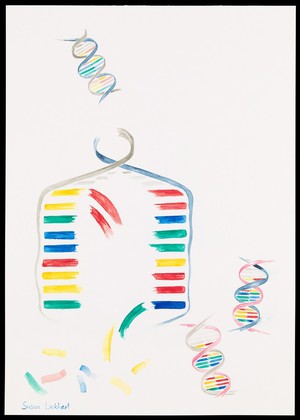
Illustration depicting semi-conservative DNA replication. A DNA double helix prior to replication is shown in the top left of the image. The sugar phosphate backbone and nucleotide bases are visible. Complementary base pairing of adenine with thymine (blue with green) and guanine with cytosine (red with yellow) is shown. During replication, a length of the double helix temporarily unwinds and separates into two strands. Free nucleotides bind by complementary base pairing to the recently exposed nucleotides on each strand which act as a template. Two new double helices are formed, each containing one original generation and one new generation strand of DNA. The sequence of base pairs in each double helix is identical to the original. Susan Lockhart. Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0). Source: Wellcome Collection.