Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
You can use this work for any purpose, as long as it is not primarily intended for or directed to commercial advantage or monetary compensation. You should also provide attribution to the original work, source and licence. Read more about this licence.
Credit
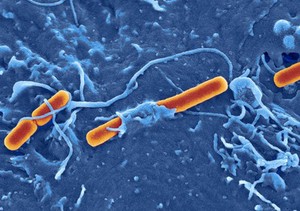
Shigella flexneri invading embryonic stem cell. David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0). Source: Wellcome Collection.