42 results filtered with: Connections

- Digital Images
- Online
Neurone development, embryoid body
John Grady, Doug Turnbull, Claudia Racca, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Insomnia
Stephen Magrath
- Digital Images
- Online
Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus, tractography
Katja Heuer and Roberto Toro
- Digital Images
- Online
Brocke and Wernicke areas of brain, MRI
Katja Heuer and Roberto Toro
- Digital Images
- Online
Insomnia
Stephen Magrath
- Digital Images
- Online
Silicon chip
Paul Griggs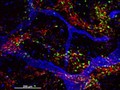
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels (string-like structures). A network of lymphatic vessels (ribbon-like structures) is also present. In this image, human skin lymphatic vessels (stained for LYVE-1; blue) and white blood cells comprised of dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) and T cells (stained for CD3; red) can be seen. Some macrophages also express the protein LYVE-1 similar to lymphatic vessel cells which can be appreciated as blue cells within and in between the sheaths of white blood cells. This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X10 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University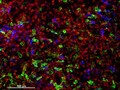
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of human skin lymphoma imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Normal human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In diseased skin, such as in skin lymphoma as seen here, this normal architecture becomes distorted. In this image, lots of T cells (stained for CD3; red), dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue) have infiltrated the skin. X20 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 100 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Silicon chip
Paul Griggs
- Digital Images
- Online
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
Ting Low
- Digital Images
- Online
Neuropil
Prof. Bill Harris
- Digital Images
- Online
Neurone development, embryoid body
John Grady, Doug Turnbull, Claudia Racca, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Neurone development, embryoid body
John Grady, Doug Turnbull, Claudia Racca, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Neurone development, embryoid body
John Grady, Doug Turnbull, Claudia Racca, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Bipolar neurone in the midbrain of an adult zebrafish, LM
Dr Mónica Folgueira
- Digital Images
- Online
Brain tractography
Katja Heuer and Roberto Toro
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. This image was taken less than 20 micrometres beneath the junction that joins the dermal and epidermal layers of the skin (dermo-epidermal junction). At this level, dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) form clusters around and between blood capillary loops (stained for CD31; red). The blind-ended tips of initial lymphatic vessels are just visible (stained for LYVE-1; blue) at this level. This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Nervous system in a fruit fly larva, serial section TEM
Albert Cardona, HHMI Janelia Research Campus
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In this image, T cells (stained for CD3; red) dendritic cells (stained for MHC class II; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue with some cells showing a tinge of green) can be seen. Cell nuclei have been stained with DAPI (grey). This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X10 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Single neurone in the midbrain of an adult zebrafish, LM
Dr Mónica Folgueira
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In this image, T cells (stained for CD3; red) dendritic cells (stained for MHC class II; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue with some cells showing a tinge of green) can be seen. Cell nuclei have been stained with DAPI (grey). This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X20 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 100 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Neuroepithelium, the developing brain
Prof. Bill Harris
- Digital Images
- Online
Purkinje neurons in culture
Annie Cavanagh
- Digital Images
- Online
Silicon chip
Paul Griggs
- Digital Images
- Online
Neural network
Arran Lewis